Understanding Blood Clots
Before we delve into the specifics of the connection between blood clots and stroke, it's important to understand what blood clots actually are. Blood clots are semi-solid masses of blood. Naturally, our blood clots to stop bleeding when we get injured. However, sometimes, blood clots can form when they're not needed and can cause serious health problems. These clots may form in various parts of our body, including the brain, which can lead to a stroke. The clot can block the flow of blood, depriving the brain of necessary oxygen and nutrients.
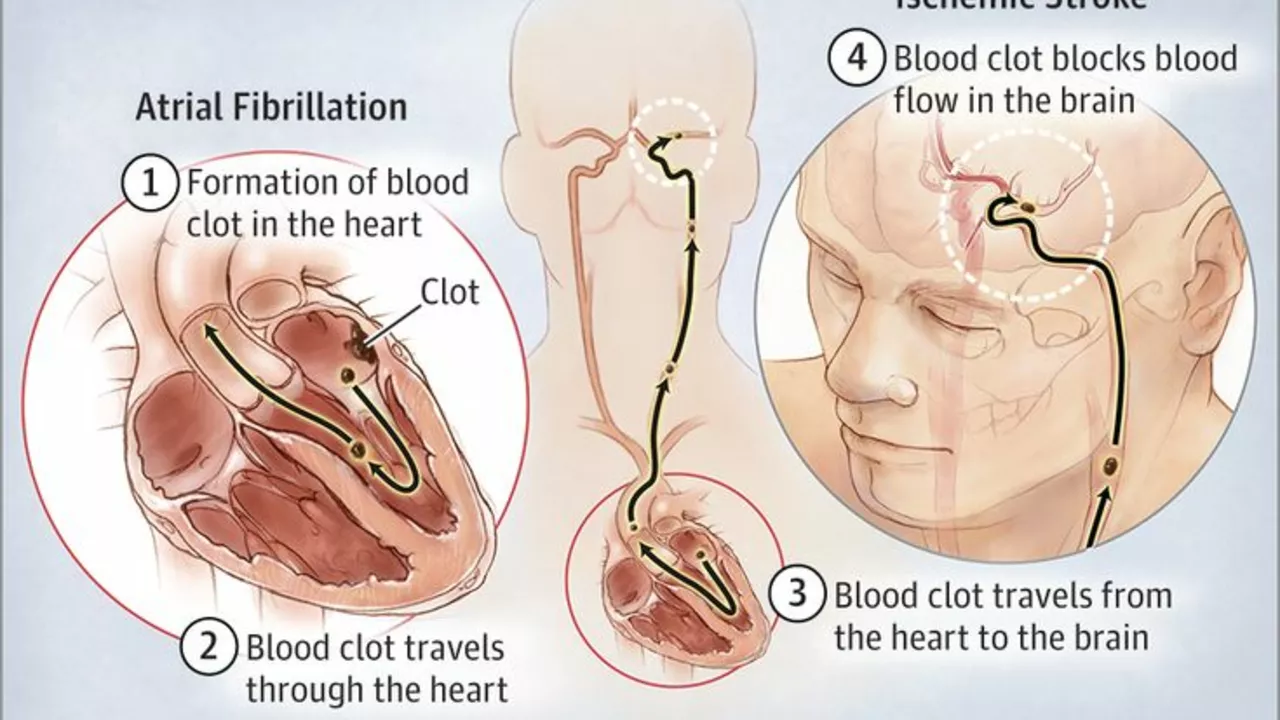
Stroke: An Overview
Stroke is a condition that affects the arteries leading to and within the brain. It's the fifth cause of death and a leading cause of disability in the United States. A stroke occurs when a blood vessel that carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain is either blocked by a clot or bursts. When that happens, part of the brain cannot get the blood (and oxygen) it needs, so it starts to die.
The Direct Connection: Blood Clots and Stroke
Now, let's talk about the direct link between blood clots and stroke. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes, which account for 87% of all strokes, occur as a result of an obstruction within a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain. This obstruction is typically a blood clot. A hemorrhagic stroke, on the other hand, occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures.
Risk Factors: What Increases Your Chances of Developing Blood Clots and Stroke
There are several factors that can increase your risk of developing a blood clot and subsequently a stroke. These include being overweight, being over 65, having a family history of stroke or blood clots, smoking, and certain medical conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and heart disease. There are also certain lifestyle factors that can increase your risk, including a poor diet, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Prevention Measures: Reducing Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke
Fortunately, there are ways to reduce your risk of developing blood clots and subsequently a stroke. This includes leading a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption. In addition, it's important to manage any medical conditions that may increase your risk, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and heart disease. Regular check-ups with your doctor can help monitor your health and manage these conditions.
Treatment Options: How to Manage Blood Clots and Stroke
There are various treatment options available for blood clots and stroke. For blood clots, these may include medications like anticoagulants and thrombolytics, as well as procedures like thrombectomy. For stroke, treatment typically involves medication to dissolve the clot and restore blood flow to the brain. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove the clot. After a stroke, rehabilitation is often necessary to help regain lost skills and function.
The Long-Term Impact: Living with the Aftermath of a Stroke
Having a stroke can have a significant impact on your life, affecting your physical, emotional, and mental health. Depending on the severity of the stroke, you may experience difficulties with movement, speech, thinking, and memory. However, with the right support and rehabilitation, it's possible to recover and lead a fulfilling life. Dealing with the aftermath of a stroke can be challenging, but remember, you're not alone. There are many resources and support networks available to help you through your recovery journey.


Ira Bliss
July 12, 2023 AT 14:31Thanks for the breakdown! 💪 Stay healthy, folks!
Donny Bryant
July 30, 2023 AT 15:51I think the article nailed the basics of clot‑related strokes. Anticoagulants like warfarin can be a real lifesaver, but they need careful monitoring. Also, staying active and keeping weight in check cuts down clot risk. Remember, every extra minute of movement helps blood flow better.
kuldeep jangra
August 17, 2023 AT 17:11First off, great job laying out the connection between clots and stroke in a clear way. Understanding that blood clots can form not just where we think, but also in hidden veins, is crucial. Many people underestimate how lifestyle factors like prolonged sitting can encourage clot formation. A sedentary job combined with a high‑fat diet creates a perfect storm for thrombosis. Moreover, genetics play a significant role; if you have a family history of clotting disorders, you should be proactive about screening. Regular check‑ups with a hematologist can catch early signs before they turn dangerous. That said, the article correctly highlights the importance of managing hypertension and cholesterol. Both conditions contribute to arterial damage, making it easier for clots to latch onto plaque. It's also worth noting that certain medications, like hormonal contraceptives, can increase clot risk, especially for women over 35. If you fall into that category, discuss alternatives with your doctor. On the prevention side, the advice to stay active is spot on-aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days. Even short walks break up long periods of sitting and stimulate circulation. Hydration is another underrated factor; proper fluid intake keeps blood viscosity lower. Lastly, the recovery part after a stroke shouldn't be brushed aside. Rehabilitation, speech therapy, and occupational therapy dramatically improve outcomes and quality of life. In summary, knowledge is power: knowing the risk factors, recognizing early symptoms, and taking preventive steps can make all the difference.
harry wheeler
September 4, 2023 AT 18:31Appreciate the thorough info, especially the emphasis on simple lifestyle changes.
faith long
September 22, 2023 AT 19:51This piece hits hard because many ignore how aggressive the body can be when it decides to clot where it shouldn't. You can't just sit there and expect miracles; you need to fight back with diet, exercise, and medical supervision. The article's call to action is spot on, but let me be crystal clear: if you think you can skip the doctor because you feel fine, you are begging for disaster. Blood clots don't ask permission, they just happen and can shut you down in minutes. So get your blood pressure checked, your cholesterol levels monitored, and don't be a hero about it. Take your meds, even if they have side effects, because the alternative could be permanent damage or death. And if you see any warning signs like sudden numbness or confusion, act FAST-call emergency services immediately.
Danny Wakefield
October 10, 2023 AT 14:30All that medical talk sounds fine until you consider that pharma companies might be hiding the real cure for clot prevention. Keep an eye on those "natural" remedies they push aside.