An Introduction to Amiloride and Its Role in Bone Health
As a health-conscious individual, I am always on the lookout for new research and discoveries that can improve our well-being. One such compound that has recently caught my attention is amiloride, a medication commonly used to treat high blood pressure and edema. In this article, I will delve into the impact of amiloride on bone health and osteoporosis, exploring various studies and findings to understand the significance of this drug on our overall health.
Understanding the Connection between Amiloride and Calcium Homeostasis
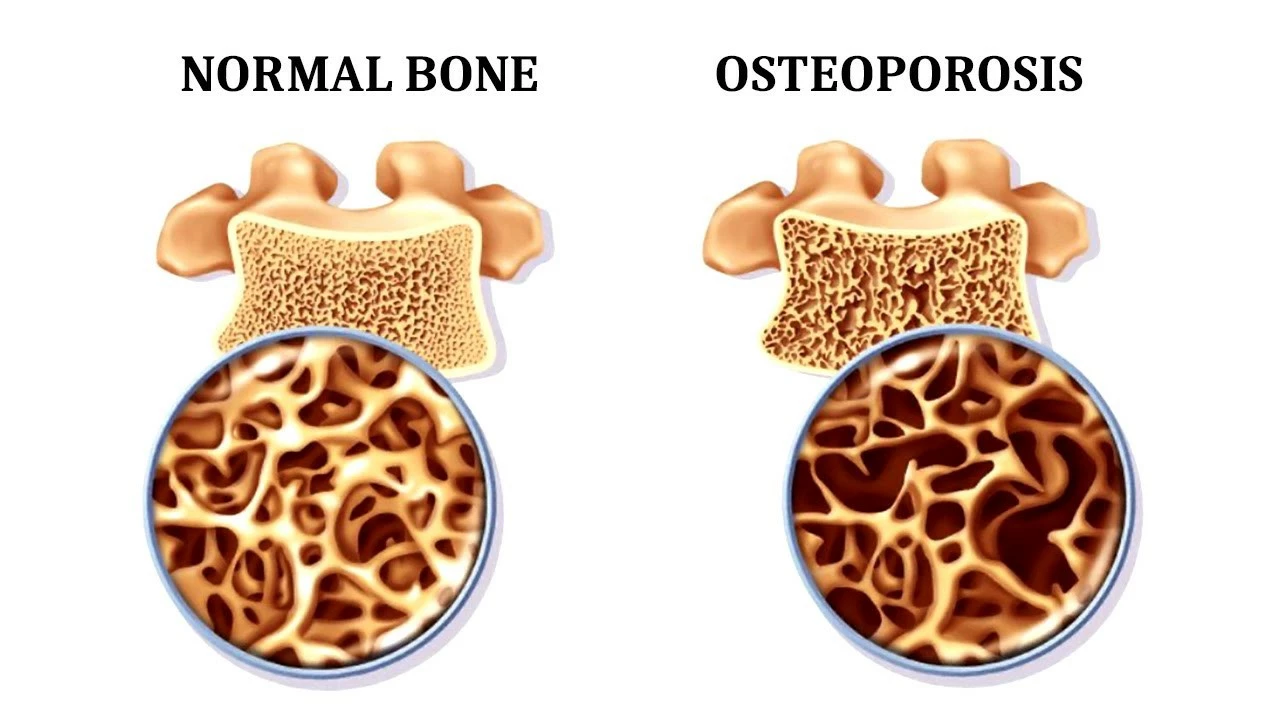
Amiloride functions as a potassium-sparing diuretic, which means it helps our bodies eliminate excess water and sodium while retaining potassium. A lesser-known aspect of this drug is its effect on calcium homeostasis – the balance of calcium levels in the body. Calcium plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. Research has shown that amiloride may help regulate calcium levels, thus playing a vital role in bone health.
Amiloride and the Epithelial Sodium Channel
One of the main mechanisms through which amiloride influences calcium homeostasis is by inhibiting the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in the kidneys. This action reduces renal calcium excretion, promoting the reabsorption of calcium into the bloodstream. As a result, amiloride helps maintain adequate calcium levels in the body, which is essential for optimal bone health.
Amiloride as a Potential Treatment for Osteoporosis
Given its positive effects on calcium homeostasis, researchers have been investigating the use of amiloride in treating osteoporosis. Studies have shown promising results, with amiloride improving bone density and reducing the risk of fractures in animal models. However, it is important to note that this research is still in its early stages, and more studies are needed to confirm these findings and determine the optimal dosage and treatment duration for humans.
Amiloride and Bone Formation
Another area of interest is the effect of amiloride on bone formation. Some studies suggest that amiloride may stimulate the activity of osteoblasts, the cells responsible for building new bone tissue. This increased bone formation could help counteract the bone loss associated with osteoporosis, further supporting the potential therapeutic use of amiloride in this condition.
Amiloride and Vitamin D Metabolism
Vitamin D is another key player in bone health, as it helps our bodies absorb calcium from the food we eat. Interestingly, amiloride has been found to influence vitamin D metabolism, potentially increasing its availability in the body. This effect could further contribute to the beneficial impact of amiloride on bone health, although more research is needed to understand the exact mechanisms involved.
Side Effects and Considerations When Using Amiloride
As with any medication, it is crucial to be aware of the potential side effects and considerations when using amiloride. Some common side effects include dizziness, headache, and gastrointestinal issues. Additionally, amiloride can cause increased potassium levels in the blood, which can be dangerous in some cases. Therefore, it is essential to closely monitor potassium levels and follow your healthcare provider's recommendations if you are taking amiloride.
Final Thoughts on Amiloride and Bone Health
While the research on amiloride and bone health is still in its early stages, the available evidence suggests that this drug could have a positive impact on calcium homeostasis, bone formation, and vitamin D metabolism. These effects may make amiloride a promising treatment option for osteoporosis and other bone-related conditions. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of the current research and approach the use of amiloride with caution until more studies are conducted to confirm its safety and efficacy in promoting bone health.


Liam McDonald
June 18, 2023 AT 22:26I appreciate the thorough overview presented here. The potential of amiloride to influence calcium homeostasis indeed merits careful consideration, especially given the delicate balance required for optimal bone metabolism. Patients should consult their physicians before modifying any regimen.
Adam Khan
June 19, 2023 AT 20:40Amiloride’s pharmacodynamic profile extends beyond its natriuretic effects, intersecting with osteogenic pathways in a manner that demands rigorous scrutiny. The inhibition of ENaC in renal tubular cells reduces calcium excretion, thereby augmenting serum calcium availability – a mechanism that has been corroborated by multiple rodent studies. Moreover, the drug’s impact on intracellular sodium gradients modulates osteoblast differentiation via the Wnt/β‑catenin cascade, a nuance often overlooked in superficial reviews. From a clinical pharmacology perspective, the dose‑response curve for bone mineral density improvement appears to plateau at sub‑hypertensive concentrations, suggesting a therapeutic window distinct from its antihypertensive use. However, the extrapolation of animal data to human physiology must be approached with caution; species‑specific variations in ENaC expression can confound translational validity. Recent meta‑analyses of the limited human trials report a modest increase in lumbar spine T‑scores, yet the confidence intervals remain wide due to heterogeneous study designs. Critics argue that the reported benefits may be attributable to concomitant potassium supplementation rather than amiloride per se. This contention underscores the necessity for double‑blind, placebo‑controlled trials with stratified cohorts. In addition, the drug’s propensity to induce hyperkalaemia imposes a safety constraint that cannot be ignored, particularly in populations with pre‑existing renal insufficiency. The interplay between elevated serum potassium and osteoclast activity is an emerging field that warrants further investigation. From an economic standpoint, repurposing amiloride for osteoporosis could be cost‑effective, given its generic status and established manufacturing pipelines. Nevertheless, regulatory hurdles persist, as the FDA requires robust evidence of bone‑specific outcomes before granting an indication change. American clinicians should remain vigilant, balancing enthusiasm for novel mechanisms with the imperative for evidence‑based practice. In sum, while the mechanistic rationale for amiloride as an adjunctive osteoporosis therapy is compelling, the current evidentiary foundation is insufficient for widespread adoption. Future research must delineate optimal dosing schedules, identify patient subgroups that derive maximal benefit, and clarify long‑term safety profiles. Only then can we responsibly integrate amiloride into the armamentarium against skeletal fragility.
rishabh ostwal
June 21, 2023 AT 00:26It is tempting to hail amiloride as a panacea for skeletal decay, yet such unbridled optimism neglects the complex etiology of osteoporosis. While the article extols calcium reabsorption via ENaC inhibition, it glosses over the systemic repercussions of chronic potassium retention. One must ask whether a modest rise in bone mineral density justifies potential cardiovascular perturbations. The drama of a single molecule reversing age‑related bone loss is, in my view, a narrative constructed more for headlines than for scientific rigor. Furthermore, the interplay between vitamin D metabolism and amiloride remains speculative at best, lacking randomized controlled data. Thus, before we embellish this diuretic with heroic status, a sober appraisal of risk‑benefit equilibrium is indispensable.
Kristen Woods
June 21, 2023 AT 01:50I must vehemently disagree with teh insinuations raised above; the evidence, though nascent, strongly indicates a net positive effect on bone integrity, and any alleged cardiovascular concerns are largely anecdotal. The omission of such data in teh original piece is a glaring oversight that undermines its credibility. Moreover, the dramatic tone employed seems designed to sow doubt rather than foster constructive discourse. It wil be imperative that we prioritize patient outcomes over speculative fears.
Carlos A Colón
June 22, 2023 AT 04:13Oh great another miracle drug for bone health.
Aurora Morealis
June 22, 2023 AT 05:36While enthusiasm is appreciated the claim lacks supporting evidence
Sara Blanchard
June 23, 2023 AT 08:00We should remember that osteoporosis affects diverse populations worldwide and that research must include varied demographic groups to ensure equitable benefits from any potential treatment like amiloride. By fostering collaborative studies across different regions and cultures we can build a more comprehensive understanding of how this medication interacts with genetic, dietary, and lifestyle factors. This inclusive approach will ultimately lead to more personalized and effective interventions for all individuals at risk of bone loss.
Anthony Palmowski
June 23, 2023 AT 09:23Exactly!!! This is why the scientific community needs to stop being so cautious!!!! We have data, we have hypotheses, and we have the right to push boundaries without endless committee meetings!!! Let's get out there and test amiloride on diverse cohorts now!!!!
Jillian Rooney
June 24, 2023 AT 11:46It is sad to see that many researchers ignore the contributions of American science in this field and rely on foreign studies that may not apply to our own populations, which ultimately harms our citizens who could benefit from homegrown solutions.